Finance is often seen as complex, technical, and reserved for professionals in suits. But in reality, finance is deeply personal. It influences how you live, what choices you make, and how secure you feel about your future. Whether you realize it or not, you interact with finance every single day—from earning money to spending it, saving it, growing it, and protecting it.
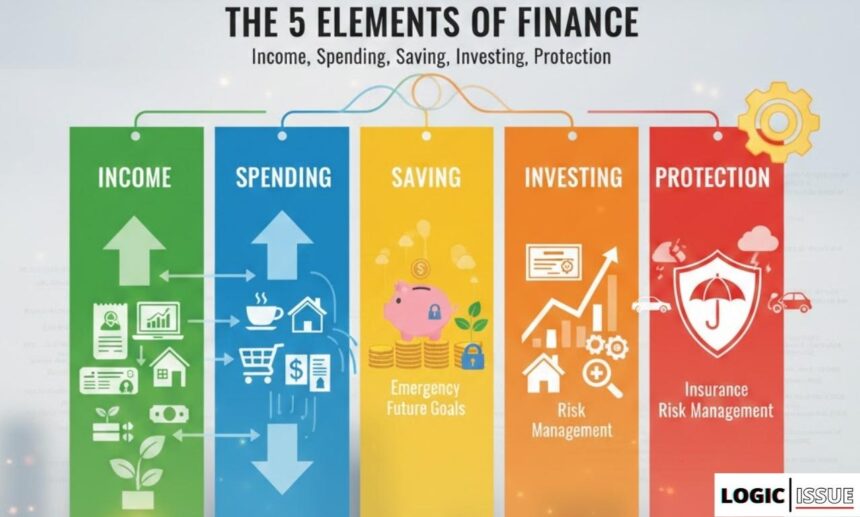
At the heart of all financial decisions lie five core elements of finance: income, spending, saving, investing, and protection. These elements apply equally to individuals, families, small businesses, and large corporations. When these elements are understood and managed properly, money becomes a powerful tool. When ignored, money becomes a constant source of stress.
In this detailed guide, we’ll break down each of the five elements of finance in simple language, using real-life examples, practical insights, and easy-to-follow explanations. By the end, you’ll not only understand what these elements are—but also how they work together to build long-term financial stability and success.
Understanding the Core Concept of Finance
Finance is the art and science of managing money. It’s about making sure the money you earn today supports your needs tomorrow. At its core, finance answers a few fundamental questions:
- How do you earn money?
- How do you use it?
- How do you prepare for the future?
- How do you grow wealth?
- How do you protect yourself from financial shocks?
The five elements of finance provide structured answers to these questions.
Element 1: Income – The Foundation of Finance
What Is Income in Finance?
Income is the money you receive from various sources. It is the starting point of all financial activity. Without income, you can’t spend, save, invest, or protect anything. Simply put, income is the fuel that powers your financial engine.
Income can come from:
- Salaries and wages
- Business profits
- Freelancing and consulting
- Rental income
- Dividends and interest
The more reliable and diversified your income, the stronger your financial base becomes.
Active Income vs Passive Income
Active income requires your time and effort. If you stop working, the income stops. Examples include jobs, hourly work, and freelancing.
Passive income, on the other hand, continues to flow with minimal daily effort. This includes rental properties, stock dividends, royalties, or automated online businesses.
A strong financial strategy aims to reduce dependency on a single active income source and gradually increase passive income streams.
Why Income Stability Matters
Income stability provides predictability. When you know how much money is coming in, planning becomes easier. You can budget confidently, save regularly, and invest strategically.
Irregular income isn’t necessarily bad, but it requires careful planning, emergency funds, and disciplined spending habits.
How to Increase Income Over Time
Income growth doesn’t always mean working longer hours. It can come from:
- Learning new skills
- Negotiating salary
- Changing careers
- Starting side hustles
- Investing in income-generating assets
Think of income as the roots of a tree—the deeper and stronger they are, the healthier the tree grows.
Element 2: Spending – Managing Where Your Money Goes
Understanding Spending in Finance
Spending represents how you use your income. Every purchase you make reflects your priorities, habits, and values. While spending is unavoidable, uncontrolled spending is one of the biggest barriers to financial success.
Fixed Expenses vs Variable Expenses
Fixed expenses stay relatively constant, such as rent, loan payments, and insurance premiums.
Variable expenses change month to month, like food, entertainment, travel, and shopping.
Understanding this distinction helps you identify where adjustments can be made during tight financial periods.
The Impact of Spending on Financial Health
You could earn a high income and still struggle financially if spending isn’t controlled. Overspending silently drains your resources, often without immediate consequences—until debt builds up.
Smart spending isn’t about cutting joy from life. It’s about spending intentionally and aligning expenses with long-term goals.
Practical Smart Spending Strategies
- Track every expense
- Use budgets as guides, not restrictions
- Avoid impulse purchases
- Prioritize value over price
- Review spending regularly
Think of spending like water flowing through pipes. If there are leaks, pressure drops everywhere else.
Element 3: Saving – Preparing for the Future
What Is Saving and Why Is It Crucial?
Saving is the act of setting aside money for future use. It’s your financial safety net and the bridge between today’s income and tomorrow’s goals.
Without savings, even small emergencies can turn into major financial crises.
Short-Term Savings vs Long-Term Savings
Short-term savings cover:
- Emergencies
- Medical bills
- Unexpected repairs
Long-term savings support:
- Buying a home
- Education
- Retirement
- Major life goals
Both are essential, and neither should be ignored.
Emergency Funds: Your Financial Shield
An emergency fund typically covers 3–6 months of living expenses. It protects you from job loss, health emergencies, or sudden income interruptions.
This fund prevents you from relying on debt during difficult times.
Common Saving Mistakes
- Saving only when money is “left over”
- Not separating savings from spending accounts
- Ignoring inflation
- Being inconsistent
Saving first—not last—is the golden rule of financial discipline.
Element 4: Investing – Growing Your Wealth
What Does Investing Mean?
Investing involves putting money into assets with the expectation of earning returns over time. Unlike saving, investing accepts some level of risk in exchange for potential growth.
Common Types of Investments
- Stocks
- Bonds
- Mutual funds
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
- Real estate
- Businesses
Each investment carries a different risk and return profile.
Understanding Risk and Return
Higher potential returns usually come with higher risk. The key is understanding your risk tolerance and investing accordingly.
Risk can be managed—not eliminated—through diversification and long-term thinking.
The Power of Compound Growth
Compound interest allows your money to grow on both the original amount and accumulated returns. Time plays a crucial role here. The earlier you invest, the more powerful compounding becomes.
Investing turns patience into profit.
Element 5: Protection – Safeguarding Financial Stability
What Is Financial Protection?
Protection focuses on minimizing financial losses caused by unexpected events. It’s often overlooked, yet it’s one of the most important elements of finance.
Insurance as a Protection Tool
Insurance transfers risk from you to an insurer. Common types include:
- Health insurance
- Life insurance
- Property insurance
- Disability insurance
Insurance doesn’t create wealth—but it protects what you’ve built.
Diversification as Risk Management
Diversifying income sources and investments reduces exposure to any single failure. If one area suffers, others can support you.
Preparing for Uncertainty
Life is unpredictable. Protection ensures setbacks don’t undo years of hard work.
How the 5 Elements of Finance Work Together
These elements don’t operate in isolation. They function as a system.
- Income funds spending and saving
- Controlled spending enables saving
- Savings support investing
- Investing grows wealth
- Protection preserves progress
Ignoring one weakens the entire structure—like removing a pillar from a building.
The Role of the 5 Elements in Personal Finance
Achieving Financial Freedom
When all five elements are balanced, financial freedom becomes achievable. You gain flexibility, confidence, and control over your future.
Improved Financial Decision-Making
Understanding finance reduces emotional decisions and increases clarity. Money choices become strategic instead of reactive.
Application of the 5 Elements of Finance in Business
Driving Business Growth
Businesses rely on these same elements to:
- Manage cash flow
- Control costs
- Plan investments
- Mitigate risks
Ensuring Long-Term Sustainability
Financially disciplined businesses survive market changes and economic downturns more effectively.
Common Mistakes People Make with the 5 Elements of Finance
- Focusing only on earning more
- Ignoring savings
- Avoiding investing due to fear
- Lacking insurance
- Short-term thinking
Awareness is the first step toward correction.
Tips to Master the 5 Elements of Finance
- Review finances monthly
- Automate savings and investments
- Increase financial literacy
- Use budgeting and tracking tools
- Think long term
Small habits, repeated consistently, create massive results.
The Future of Finance and Its Core Elements
Technology is reshaping how we manage money. Digital banking, automation, and financial apps make managing these elements easier than ever.
However, the core principles remain unchanged. Tools evolve, but fundamentals stay the same.
Conclusion
The five elements of finance—income, spending, saving, investing, and protection—are the pillars of financial success. Mastering them doesn’t require advanced degrees or complex strategies. It requires awareness, discipline, and consistency.
When these elements work in harmony, money becomes a resource—not a worry. Whether you’re just starting out or refining your financial journey, understanding and applying these five elements can transform your financial future.
FAQs

1. What are the five elements of finance?
Income, spending, saving, investing, and protection.
2. Why are these elements important?
They help manage money effectively and ensure long-term financial stability.
3. Which element should I focus on first?
Income is the starting point, but balance across all five is essential.
4. Is investing necessary for financial success?
While not mandatory, investing significantly accelerates wealth creation.
5. How can beginners apply the five elements of finance?
Start with budgeting, build savings, invest gradually, and protect against risks.
See Also: Security in Banking: Protecting Your Financial Assets